Customer - Top Tips - Market trends and forcasts
Market trends and forcasts
This document is designed as a quick reference guide to trend analysis.
This will enable you to gain knowledge of a particular skill, task or process in store. This means you can quickly find the key information that you need and refer to it on an ongoing basis whenever you need to refresh your knowledge.
Introduction
The term 'trend analysis' refers to the concept of collecting information and attempting to spot a pattern, or trend, in the information.
Trend analysis can be used to draw conclusions about what’s happened in the past and can help us to forecast future events.
It’s a great way of pulling together lots of individual pieces of data so as to make the information more meaningful. For example; rather than looking at sales or margin figures in isolation we would look at the same figure from last week/period/quarter/year to get an overall view of performance. When plotted on a graph such as the simplified example below, we can easily identify areas where performance is increasing or decreasing and begin to consider the reasons for this and how this may continue or change in the future.
Customer - Top Tips - Market trends and forcasts
What you need to know
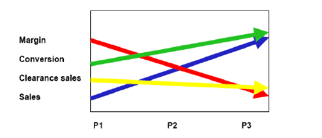
Getting a good understanding of market trends is important if we are to make the most of our opportunities and remain competitive. As well as looking at data relating to our own performance, it’s also useful to understand how our competitors are doing and use this information to think about what they might do next.
When pulling data together to identify trends and product forecasts it’s worth considering the following questions…
● What demand exists for your product/service – is it grow or declining?
● What general economic trends exist and to what extent will this impact performance in your area?
● What new products are coming onto the market that will engage our customers? Will they be exclusive to us or our suppliers and what impact will this have?
● What are your competitors doing? What plans do they have in place? Do they have any promotions coming up?
Customer - Top Tips - Market trends and forcasts
What you need to know
Interpreting Market Data
There are many sources of data that you can use to keep up to date with market trends and when doing so you should be aware of the following to ensure accuracy.
● External data may have been gathered for a purpose other than that which you are using it for, or not apply to the specific market you are working within
● Check how recent and therefore valid the information you are using is. It can be difficult to tell how recent some information (e.g. online) is
● When working with figures, averages can be misleading. Combine the use of statistics with other forms of information and be aware when you are working with averages
● Make sure you look at a full range of market data and avoid searching for information that simply supports a predetermined conclusion (you may not even realise that you’re doing this)
Market Forecasting
Researching and forecasting the market helps inform our business decisions such as bringing new products to market, withdrawing products from the market and managing the promotional mix.
Forecasting can be carried out at a macro and micro level. Macro forecasting looks at the markets as a whole to establish current demand and likely levels of demand in the future. Micro forecasting is focused on the detail of unit sales forecasts, establishing the products current market share and what could happen to this in the future.
The following factors will determine which type of forecasting is most appropriate to use:
● Accuracy – if the decisions that will be made as a result of the forecast are high risk decisions, then the forecast must be as accurate as possible and this may require a greater investment of time and money
● Availability – in some markets there is a wealth of information and in others it is harder to find
● Timespan – are you producing a short term or long term forecast
● Product Life Cycle – less information will be available relating to products at the ‘introductory’ stage of the product life cycle, compared to products at the ‘maturity’ stage.
Creating the Sales Forecast for a Product
There are several stages to follow when creating a forecast…
1. Estimate market demand (the total volume to be bought by a defined customer group in a defined geographical area and time period). You need to know actual industry sales taking place in the market, which involves identifying competitors and estimating their sales. This information is often available from industry trade associations and market research firms.
1. Estimate Company demand (the company’s share of market demand).
Having estimated market demand you can evaluate our performance against the whole market and identify our market share. This is largely dependent on how we are perceived in relation to our competitors.
1. Develop the sales forecast (the level of sales we expect to achieve taking into account our marketing plan and environment). A common approach to take when developing a forecast is to begin looking at the economic environment as a whole and what is likely to happen moving forward. Then consider the impact of this on the overall sales in the industry and then drill down into what this means in terms of sales for the company. This should be based on what you know about your customers buying behaviours both in the present and looking at past trends.
When developing the sales forecast, you may come across the term time series analysis, which involves analysing past sales performance, looking at:
● Trend – are sales growing, declining or staying about the same (flat lining)
● Seasonal – product sales vary according to the time of year and this trend repeats each year e.g. imaging product sale increase during spring/summer as our customers get ready for their summer holidays
● Unexpected/irregular events – such as fashion fads, freak weather conditions and sporting events such as world cups can drive a sales increase or decline in some product categories. When comparing year on year data the impact of such events in the previous year’s needs to be stripped out as far as possible
● Results – of specific activities taken to drive sales increase e.g. new advertising campaign or special promotion. Again, this needs to be taken into account when comparing year on year data, as this year we may not have a new advertising campaign for example.
Summary
Analysing trends and creating forecasts provide important insights into our market and overall performance to inform future decisions.
Forecasting can be challenging, as there are so many influencing factors to be considered, and anticipating the impact of these often proves difficult.
The risk of inaccuracy can be mitigated somewhat by carefully considering the data used how it’s interpreted and the level and type of forecasting that is most appropriate.